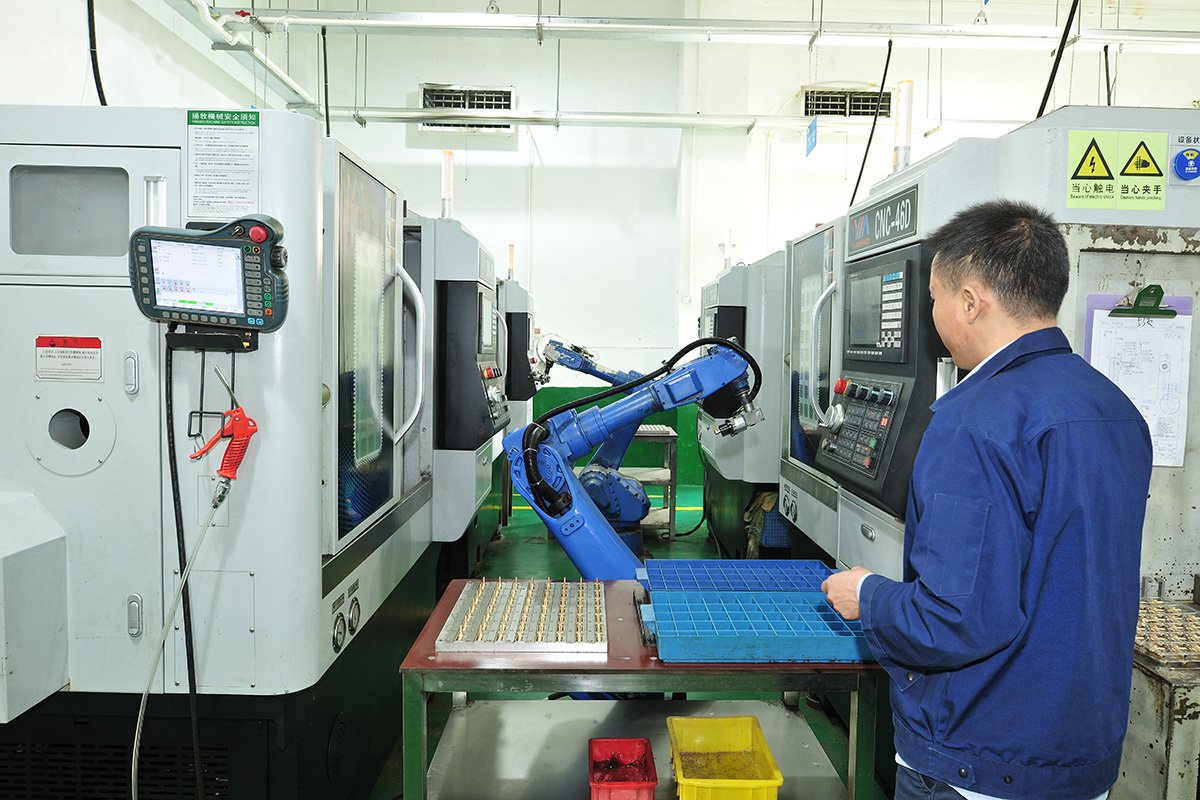
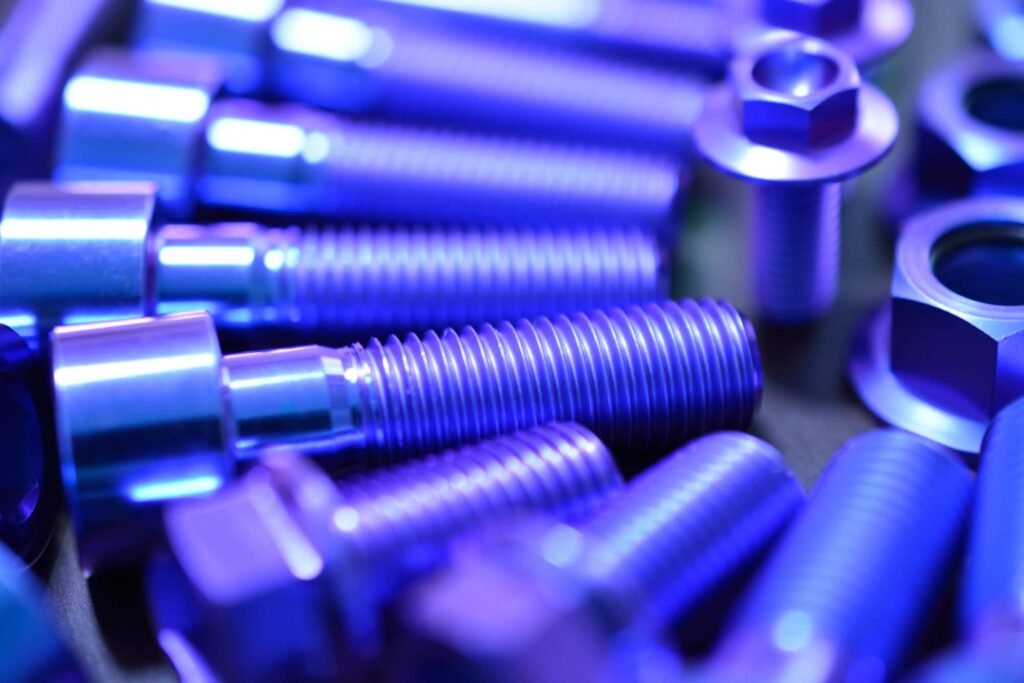
Why do custom mechanical parts use metal surface treatment? What are the benefits of using metal surface treatment on mechanical parts? To improve the durability (corrosion protection), appearance, and functionality of the product. Engineers usually perform additional surface treatment on part or all of the outer surfaces of metal parts after processing or manufacturing. These surface treatment processes include anodizing, nickel plating, galvanizing, blackening, electrolytic polishing, sandblasting, polishing, passivation, dacromet, powder coating, painting, PVD, etc.
Anodizing and Hard Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. It’s commonly used for aluminum, enhancing its natural oxide layer. Hard anodizing, a variant, provides an even more robust surface, ideal for applications requiring extreme wear resistance.
Benefits of Anodizing:
- Corrosion Resistance: Protects against environmental degradation.
- Aesthetic Versatility: Offers a range of color options through dyeing.
- Increased Surface Hardness: This is especially true with hard anodizing, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Nickel Plating
Nickel plating involves depositing a layer of nickel onto a substrate, offering excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It’s often used in combination with other metals for enhanced properties.
Key Advantages:
- Corrosion Protection: Especially in harsh environments.
- Improved Wear Resistance: Extends the life of components.
- Aesthetic Enhancement: Provides a shiny, decorative finish.
Common Uses:
- Automotive parts
- Kitchen appliances
- Jewelry
Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is a cost-effective method of providing corrosion resistance to steel and iron components. The zinc acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding before the underlying metal.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Affordable protection against rust.
- Versatile: Can be applied to a wide range of components.
- Enhanced Durability: Prolongs the life of metal parts.
Typical Applications:
- Fasteners
- Automotive components
- Construction hardware
Black Oxide
Black oxide treatment is a conversion coating for ferrous materials, stainless steel, copper, and copper-based alloys. It provides a sleek black finish and enhances corrosion resistance.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Provides a uniform black finish.
- Corrosion Resistance: Offers moderate protection against rust.
- Reduced Light Reflection: Ideal for optical and military applications.
Applications:
- Firearms
- Tools
- Machinery parts
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes material from a metallic surface, resulting in a smooth, polished finish. It’s often used for stainless steel and other metals.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Corrosion Resistance: Removes impurities and enhances surface quality.
- Aesthetic Enhancement: Provides a bright, reflective finish.
- Microfinish Improvement: Reduces surface roughness.
Common Uses:
- Medical devices
- Food processing equipment
- Pharmaceutical machinery
Blasting
Blasting involves propelling abrasive material against a surface to clean, smooth, or shape it. It’s a versatile process used in various industries for surface preparation.
Advantages:
- Surface Preparation: Ideal for cleaning and preparing surfaces for further treatment.
- Versatility: Suitable for different materials and applications.
- Improved Adhesion: Enhances the bonding of coatings and paints.
Applications:
- Automotive restoration
- Metal fabrication
- Construction
Polishing
Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing it or using a chemical action. It’s essential for both aesthetic and functional purposes.
Benefits:
- Aesthetic Appeal: Provides a high-gloss finish.
- Smooth Surface: Reduces friction and wear.
- Enhanced Cleanability: Easier to maintain and clean.
Typical Uses:
- Jewelry
- Automotive parts
- Consumer electronics
Passivation
Passivation is a chemical treatment for stainless steel and other metals to enhance their corrosion resistance. It involves removing free iron from the surface, forming a passive oxide layer.
Advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Protects against rust and oxidation.
- Extended Durability: Increases the lifespan of components.
- Improved Cleanliness: Removes contaminants and impurities.
Applications:
- Medical instruments
- Aerospace components
- Food processing equipment
Dacromet
Dacromet is a proprietary coating process that provides superior corrosion protection, especially for steel. It involves applying a zinc and aluminum flake coating.
Benefits:
- High Corrosion Resistance: Outperforms traditional zinc plating.
- Environmentally Friendly: Free of heavy metals.
- Heat Resistance: Suitable for high-temperature applications.
Common Uses:
- Automotive fasteners
- Wind turbine components
- Construction materials
Powder Coating
Powder coating is a dry finishing process that involves applying a free-flowing powder to a surface, which is then cured under heat. It’s known for its durability and vibrant colors.
Key Advantages:
- Durability: Resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading.
- Environmental Benefits: Emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Aesthetic Versatility: Available in a wide range of colors and finishes.
Applications:
- Household appliances
- Outdoor furniture
- Automotive parts
Painting
Painting is one of the most common surface treatments, providing both aesthetic and protective benefits. It involves applying a liquid coating that dries to form a solid film.
Benefits:
- Aesthetic Enhancement: Offers infinite color possibilities.
- Corrosion Protection: Shields against environmental factors.
- Versatility: Suitable for various materials and surfaces.
Typical Uses:
- Buildings and structures
- Vehicles
- Machinery
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
PVD is a vacuum coating process that produces a thin film on the surface of a material. It’s used for decorative and functional purposes, providing a durable and wear-resistant finish.
Advantages:
- Wear Resistance: Extends the life of components.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Offers a range of colors and finishes.
- Environmentally Friendly: Produces minimal waste.
Applications:
- Cutting tools
- Watches and jewelry
- Automotive components
Conclusion
Material surface treatments are integral to modern manufacturing, providing solutions that enhance durability, aesthetics, and functionality. From anodizing and plating to blasting, each process provides unique benefits tailored to specific applications. By understanding and utilizing the right surface treatment, manufacturers can significantly improve the performance and longevity of their products.
To explore more about these processes or find the right solution for your needs, consider reaching out to us or emailing lynn@gmprecnc.com.
Key Automotive Components That Rely on CNC Machining
Everything You Need To Know About Anodizing







