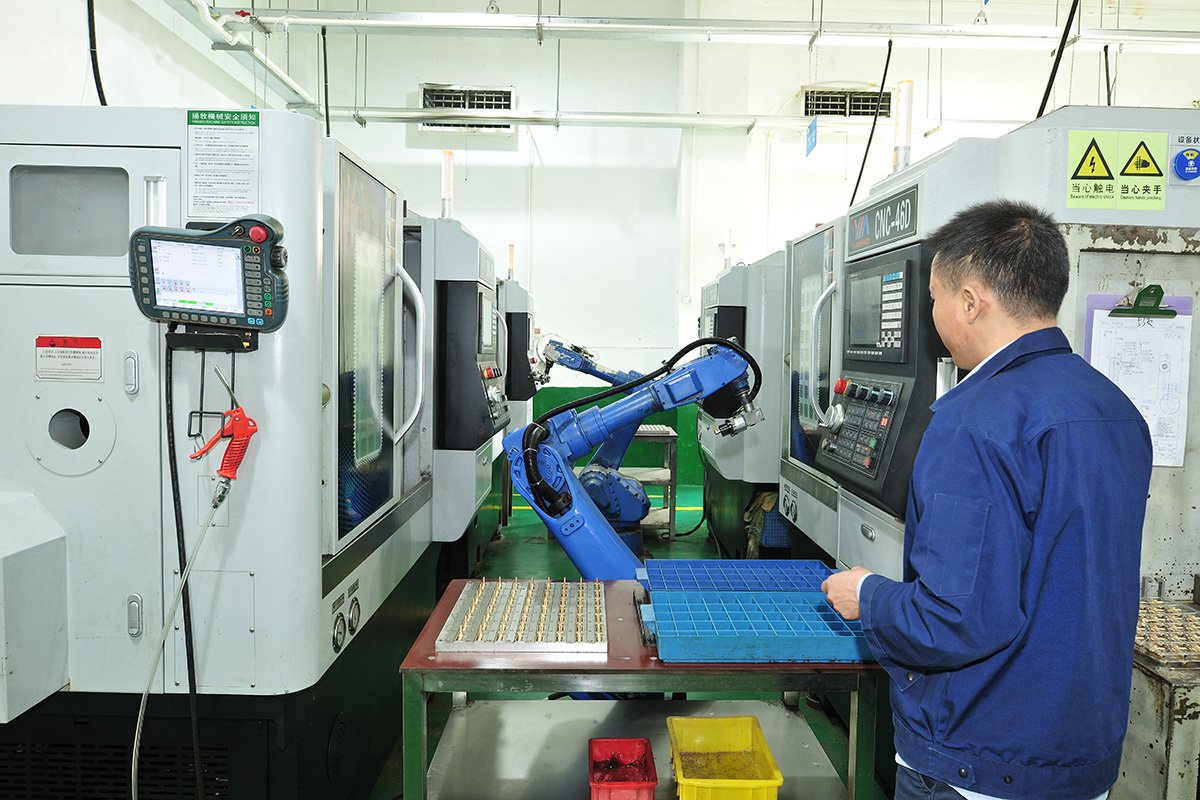
In modern manufacturing, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology stands as a beacon of precision and efficiency. Industries rely on CNC turning, milling, and advanced 5-axis CNC milling to create intricate parts with unparalleled accuracy.
Understanding CNC Turning and Milling
CNC Turning: The Art of Rotational Symmetry
CNC turning is a process where a rotating workpiece is shaped using stationary cutting tools. This method is ideal for creating cylindrical components such as shafts, bushings, and fasteners. The process involves:
- High Accuracy and Repeatability: CNC turning offers precision with tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm.
- Material Versatility: CNC turning is a versatile choice for various industries, as it can handle metals, plastics, and composites.
- Efficiency in Production: Particularly cost-effective for high-volume runs, making it a preferred method for producing rotationally symmetric parts.

CNC Milling: Crafting Complexity with Rotating Tools
CNC milling employs rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece, allowing for the creation of complex geometries. Key features include:
- 3-Axis to 5-Axis Capabilities: While traditional 3-axis milling is suitable for simpler designs, 5-axis milling allows for more intricate parts by enabling movement along five axes.
- Diverse Material Options: From aluminum to titanium, CNC milling can process a wide range of materials, making it ideal for industries such as aerospace and medical devices.
- Surface Finish and Detail: CNC milling can achieve high-quality surface finishes, essential for parts requiring both aesthetic appeal and functional precision.

The difference between CNC milling and turning
Motion & Cutting Action:
- Turning: The workpiece spins while a stationary cutting tool moves linearly to remove material radially or axially.
- Milling: The cutting tool spins while the workpiece is fixed (or moves incrementally) to cut material from multiple angles.
Workpiece Geometry:
- Turning excels at creating rotationally symmetric parts (e.g., rods, cones, disks).
- Milling handles complex prismatic parts with contours, slots, pockets, or 3D surfaces.
Tooling:
- Turning uses single-point tools for continuous cuts.
- Milling uses multi-point tools (end mills) for interrupted cuts.
Axes of Movement:
- Basic turning: 2 axes (X, Z).
- Basic milling: 3+ axes (X, Y, Z ± rotational).
Setup:
- Turning: Workpiece held in a chuck or collet.
- Milling: Workpiece fixed to a bed or vise.
Hybrid Machines:
Mill-Turn Centers: Combine both technologies. The workpiece can rotate (like turning) while milling tools operate on it, enabling complex parts (e.g., camshafts) in one setup.
When to Use Which:
Choose Turning for:
Cylindrical parts, rotational symmetry, threads, grooves.
Example: A car axle.
Choose Milling for:
Flat surfaces, slots, pockets, complex 3D shapes.
Example: An engine block.
Summary:
Turning = Rotating workpiece + stationary tool → Cylindrical parts.
Milling = Rotating tool + stationary workpiece → Complex 3D parts.
Application
CNC Mill Applications
- Engine parts
- Gears
- Fittings
- Medical instruments
- Brackets
- Enclosures
- Water pumps, etc.
CNC Turn Applications
- Crankshaft
- Camshaft
- Piston pin
- Valve guide
- Gear blank
- Drive shaft
- Hydraulic joint
- Threaded pipe fittings
- Flange
- Surgical instrument handle
- Implant base
- Connector housing
- Pump shaft
- Sealing ring
- Valve core
The Leap to 5-Axis CNC Milling
CNC turning centers are advanced computer numerically controlled machine tools. They can be equipped with 3, 4, or even 5 axes and have a variety of cutting functions. 5-axis CNC milling represents a significant advancement in machining technology, offering several advantages over traditional methods:
- Complex Geometries: Capable of machining intricate designs from any angle, reducing the need for multiple setups.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Minimizes handling errors, improving the overall precision of the finished product.
- Improved Surface Finish: Maintains optimal tool angles relative to the surface, enhancing quality and reducing secondary finishing operations.
Applications of 5-Axis CNC Milling
5-axis CNC milling is extensively utilized in various industries due to its versatility:
- Aerospace Components: Crafting airframe structures and engine parts with complex contours.
- Automotive Parts: Producing transmission gears and engine mounts with intricate features.
- Medical Implants: Manufacturing bespoke implants such as hip joints and cranial plates.
The Role of Anodizing in CNC Machining
Anodizing is a surface finishing process that enhances the properties of CNC machined parts, particularly those made from aluminum. The benefits include:
- Increased Corrosion Resistance: Anodizing creates a protective oxide layer, extending the part’s lifespan.
- Wear Properties: Improves wear resistance, making parts more durable under stress.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Allows for color dyeing, offering both functional and decorative benefits.
Insights from Industry Leaders
Companies like RapidDirect and Astro Machine Works exemplify excellence in CNC machining. RapidDirect offers instant CNC quotes and a wide array of materials, while Astro Machine Works boasts over three decades of expertise in 5-axis machining. Their commitment to precision and innovation underscores the transformative power of CNC technology in modern manufacturing.
Best Practices for CNC Machining
To optimize CNC machining processes, consider the following guidelines:
- Design Considerations: Ensure parts have adequate thickness and avoid sharp inside corners to facilitate machining.
- Material Selection: Choose materials that align with the desired properties and machining capabilities.
- Surface Finishes: Select appropriate finishing options, such as anodizing or polishing, to enhance part performance and appearance.
Conclusion: The Future of Manufacturing
CNC turning and milling are pivotal in shaping the future of manufacturing. By harnessing these technologies, industries can achieve unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency. As you explore the possibilities of CNC machining, consider partnering with experienced providers to bring your designs to life with accuracy and speed.
A Deep Dive into 5-Axis CNC Milling Services